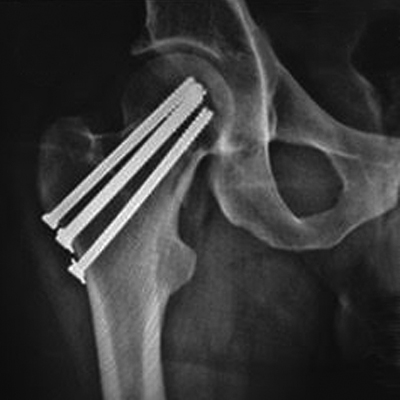
Tratamiento de las fracturas de cuello femoral con osteosíntesis. Diez claves para el éxito Diez claves para el éxito
Contenido principal del artículo
Resumen
Descargas
Métricas
Detalles del artículo
La aceptación del manuscrito por parte de la revista implica la no presentación simultánea a otras revistas u órganos editoriales. La RAAOT se encuentra bajo la licencia Creative Commons 4.0. Atribución-NoComercial-CompartirIgual (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/deed.es). Se puede compartir, copiar, distribuir, alterar, transformar, generar una obra derivada, ejecutar y comunicar públicamente la obra, siempre que: a) se cite la autoría y la fuente original de su publicación (revista, editorial y URL de la obra); b) no se usen para fines comerciales; c) se mantengan los mismos términos de la licencia.
En caso de que el manuscrito sea aprobado para su próxima publicación, los autores conservan los derechos de autor y cederán a la revista los derechos de la publicación, edición, reproducción, distribución, exhibición y comunicación a nivel nacional e internacional en las diferentes bases de datos, repositorios y portales.
Se deja constancia que el referido artículo es inédito y que no está en espera de impresión en alguna otra publicación nacional o extranjera.
Por la presente, acepta/n las modificaciones que sean necesarias, sugeridas en la revisión por los pares (referato), para adaptar el trabajo al estilo y modalidad de publicación de la Revista.
Citas
management of fractures of the neck of the femur. Injury 1989;20(2):101-5. https://doi.org/10.1016/0020-1383(89)90152-6
2. Loizou M, Parker J. Avascular necrosis after internal fixation of intracapsular hip fractures; a study of the outcome for 1023 patients. Injury 2009;40(11):1143-6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2008.11.003
3. Upadhyay A, Jain P, Mishra P, Maini L, Gautum VK. Delayed internal fixation of fractures of the neck of the femur in young adults. A prospective, randomised study comparing closed and open reduction. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2004;86(7):1035-40. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620x.86b7.15047
4. Papakostidis C, Panagiotopoulos A, Piccioli A, Giannoudis P. Timing of internal fixation of femoral neck fractures. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the final outcome. Injury 2015;46(3):459-66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2014.12.025
5. Pereira S, Calvo X, Lugones A, Vindver G, Bidolegui F. Osteosíntesis con tornillos canulados en fracturas mediales de cadera Factores pronósticos y resultados en 93 casos Rev Asoc Argent Ortop Traumatol 2014;79(1):27-34. https://www.aaot.org.ar/revista/2014/n1/Rev_Asoc_Argent_Ortop_Traumatol_2014_79_(1)_27-34_Pereira.pdf
6. Egol K, Koval KJ, Oh CK. Does a traction-internal rotation radiograph help to better evaluate fractures of the
proximal femur? Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis 2008;66(2):102-6. PMID: 18537778
7. Temmesfeld M, Dolatowski FC, Borthne A, Utvag SE, Hoelsbrekken SE. Cross-table lateral radiographs accurately predict displacement in valgus-impacted femoral neck fractures. J Bone Joint Surg 2019:e0037.
https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.OA.18.00037
8. Frandsen P, Andersen P, Christoffersen H, Per B. Thomsen osteosynthesis of femoral neck fracture: The slidingscrew-plate with or without compression. Acta Orthop Scand 1984;55(6):620-3. https://doi.org/10.3109/17453678408992408
9. Huang TW, Hsu WH, Peng KT, Lee CY. Effect of integrity of the posterior cortex in displaced femoral neck fractures on outcome after surgical fixation in young adults. Injury 2011;42(2):217-22.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2010.10.005
10. Rawall S, Bali K, Upendra B, Garg B, Yadav CS, Jayaswal A. Displaced femoral neck fractures in the young:
significance of posterior comminution and raised intracapsular pressure. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2012;132:73-9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-011-1395-1
11. Rikli D, Goldhahn S, Blauth M, Mehta S, Cunningham M. PIP Study group. Optimizing intraoperative imaging during proximal femoral fracture fixation - A performance improvement program for surgeons. Injury 2018;49(2):339-44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2017.11.024
12. Poyanli OS, Soylemez S, Ozkut AT, Uygur E, Kemah B. Precise placement of lag screws in operative treatment of trochanteric femoral fractures with a new guide system Injury 2015;46(11):2190-95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2015.06.003
13. Yang J, Lin L, Chao K, Chuang S, Wu C. Risk factors for nonunion in patients with intracapsular femoral neck
fractures treated with three cannulated screws placed in either a triangle or an inverted triangle configuration. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2013;95(1):61-9. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.K.01081
14. Florschutz A, Langford J, Haidukewych G, Koval K. Femoral neck fractures: current management. J Orthop
Trauma 2015;29(3):121-9. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOT.0000000000000291
15. Chua D, Jaglal SB, Schatzker J. Predictors of early failure of fixation in the treatment of displaced subcapital hip fractures. J Orthop Trauma 1998;12(4):230-4. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005131-199805000-00002
16. Krischak G , Beck A, Wachter N, Jakob R, Kinzl L, Suger G. Relevance of primary reduction for the clinical
outcome of femoral neck fractures treated with cancellous screws. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2003;123(8):404-
9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-003-0571-3
17. Su Y, Chen W, Zhang Q, Li B, Guo M. An irreducible variant of femoral neck fracture: A minimally traumatic
reduction technique. Injury 2011;42(2):140-5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2010.05.008
18. Yu S, Xu X, Pandey N, Zhao Y, Jing J. A safe percutaneous technique for the reduction of irreducible femoral
neck fractures using ultrasound localization of the femoral vascular and nervous structures at the hip. Medicine
(Baltimore) 2019;98(15): e15163. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000015163
19. Mahajan RH, Kumar S, Mishra B. Technique for gentle accurate reproducible closed reduction of intracapsular
fracture of neck of femur. Injury 2017;48(3):789-790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2016.10.030
20. Watson-Jones R. Fractures of the neck of the femur. Br J Surg 1936;23(92):787-808. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.1800239213
21. Smith-Petersen MN. A new supra-articular subperiosteal approach to the hip joint. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1917;s2-15(8):59222. Slobogean GP, Sprague SA, Scott T, McKee M, Bhandari M. Management of young femoral neck fractures: is there a consensus? Injury 2015;46(3):435-40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2014.11.028
23. Molnar RB, Routt ML. Open reduction of intracapsular hip fractures using a modified Smith-Petersen surgical
exposure. J Orthop Trauma 2007;21(7):490-4. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOT.0b013e31804a7f7f
24. Lichstein P, Kleimeyer J, Githens M, Vorhies J, Gardner M, Bellino M, et al. Does the Watson-Jones or modified
Smith-Petersen approach provide superior exposure for femoral neck fracture fixation? Clin Orthop Relat Res
2018;476(7):1468-76. https://doi.org/ 10.1097/01.blo.0000533627.07650.bb
25. Giannoudis P, Panteli M. Biomechanical rationale for implant choices in femoral neck fracture fixation in the nonelderly. Injury 2015;46(3):445-52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2014.12.031
26. Bhandari M, Tornetta P 3rd, Hanson B, Swiontkowski M. Optimal internal fixation for femoral neck fractures:
multiple screws or sliding hip screws? J Orthop Trauma 2009;23(6):403-7. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOT.0b013e318176191f
27. Wu-ren Hou, Min-ou Xu. [Comparison among three cannulated screws and dynamic hip screw combined with
antirotation screw for comminuted fractures of femoral neck]. China J Orthop Traumatol 2015;28(9):796-801. [En
chino] PMID: 26647559.
28. Cha Y, Yoo J, Wang S, Kim K, Choy W, Hwang S. Biomechanical evaluation of internal fixation of Pauwels type III femoral neck fractures: A systematic review of various fixation methods. Clin Orthop Surg 2019;11(1):1-14.
https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2019.11.1.1
29. Fixation using Alternative Implants for the Treatment of Hip fractures (FAITH) Investigators. Fracture fixation in the operative management of hip fractures (FAITH): an international, multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2017;389(10078):1519-27. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30066-1
30. Ma J, Kuang M, Xing F, Zhao Y, Chen H, Zhang L. Sliding hip screw versus cannulated cancellous screws for
fixation of femoral neck fracture in adults: A systematic review. Int J Surg 2018;52:89-97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2018.01.050
31. Kloen P, Rubel I, Lyden J, Helfet D. Subtrochanteric fracture after cannulated screw fixation of femoral neck
fractures: A report of four cases. J Orthop Trauma 2003;17(3):225-9. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005131200303000-00013
32. Sensoz E, Mehmet F, Acar V. Finite element analysis of the impact of screw insertion distal to the trochanter minor on the risk of iatrogenic subtrochanteric fracture. Proc Inst Mech Eng H 2018;232(8):807-18. https://doi.org/10.1177/0954411918789963
33. Swiontkowski MF, Harrington RM, Keller TS. Torsion and bending analysis of internal fixation techniques for
femoral neck fracture: the roll of implant design and bone density. J Orthop Res 1987;5:433-44. https://doi.org/10.1002/jor.1100050316
34. Maurer S, Wright K, Koval K, Zuckerman F. Two or three screws for fixation of femoral neck fractures? Am J
Orthop (Belle Mead NJ) 2003;32(9):438-42. PMID: 14560825
35. Krastman P, van den Bent RP, Krijnen P, Schipper IB. Two cannulated hip screws for femoral neck fractures:
treatment of choice or asking for trouble? Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2006;126(5):297-303. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-006-0143-4
36. Zlowodzki M, Weening B, Petrisor B, Bhandari M. The value of washers in cannulated screw fixation of femoral neck fractures. Trauma 2005;59(4):969-75. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ta.0000188130.99626.8c
37. Zlowodzki M, Wijdicks C, Armitage B, Cole A. Value of washers in internal fixation of femoral neck fractures with cancellous screws: a biomechanical evaluation. J Orthop Trauma 2015;29(2):e69-72. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOT.0000000000000172
38. Selvan VT, Oakley J, Rangan A, Al-Lami MK. Optimum configuration of cannulated hip screw for the fixation of
intracapsular hip fracture: a biomechanical study. Injury 2004;35(2):136-41. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0020-1383(03)00059-7
39. Guo I, Dong W, Qin S, Zhang Y. Definition of ideal configuration for femoral neck screw fixation in older people. Sci Rep 2019;9:12895. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-48258-2
40. Gümüştaş SA, Tosun HB, Ağır İ, Orak MM, Onay T, Okçu G. Influence of number and orientation of screws on
stability in the internal fixation of unstable femoral neck fractures. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc 2014;48(6):673-8.
https://doi.org/10.3944/AOTT.2014.14.0088
41. Collinge C, Mir H. Application of a medial buttress plate may prevent many treatment failures seen after fixation of vertical femoral neck fractures in young adults. Med Hyp 2015;84(5):429-33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2015.01.029
42. Ye Y, Chen K, Tian K, Li W, Mauffrey C, Hak DJ. Medial buttress plate augmentation of cannulated screw fixation in vertical unstable femoral neck fractures: surgical technique and preliminary results. Injury 2017;48(10):2189-93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2017.08.017
43. Hoffman J, Kellam J, Routt C, Gary J. Is the cranial and posterior screw of the “inverted triangle” configuration for femoral neck fractures safe? J Orthop Trauma 2019;33(7):331-4. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOT.0000000000001461
44. Gurusamy K, Parker MJ, Rowlands TK. The complication of displaced intracapsular fractures of the hip. The effect of screw positioning and angulation on fracture healing. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2005;87:632-4.
https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.87B5.15237
45. Ly TV, Swiontkowski MF. Treatment of femoral neck fractures in young adults. Instr Course Lect 2009;58:69-81. PMID: 19385521
46. Triplet JJ, Sullivan B, Taylor BC. The influence of capsulotomy for intracapsular hip fractures. J Long Term Eff Med Implants 2018;28(3):187-92. https://doi.org/10.1615/JLongTermEffMedImplants.2018028556