El Uso de la escala LRINEC en pacientes con infecciones necrosantes en el miembro superior y su correlación con la morbimortalidad ortopédica
Contenido principal del artículo
Resumen
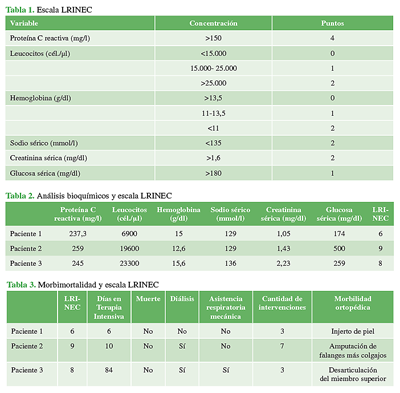
Materiales y Métodos: Se llevó a cabo una revisión sistemática de las historias clínicas de los pacientes operados por nuestro equipo, entre el 1 de marzo de 2015 y el 1 de marzo de 2020. Se registraron los puntajes de la escala LRINEC de cada paciente operado con diagnóstico clínico y posoperatorio de infección necrosante de partes blandas, así como sus antecedentes clínicos, el microorganismo, las complicaciones y la morbimortalidad ortopédica, y otros datos clínicos importantes (tiempo de internación en terapia intensiva, necesidad de asistencia respiratoria mecánica y de diálisis, cantidad de cirugías), y se los comparó con el puntaje.
Resultados: Se analizaron 4126 historias clínicas de pacientes operados por nuestro equipo. Tres tuvieron infecciones necrosantes del miembro superior. El puntaje aplicado en forma retrospectiva determinó que todos tenían una alta probabilidad de sufrir una infección necrosante. Los pacientes con puntaje más alto desarrollaron más comorbilidades ortopédicas y clínicas.
Conclusiones: La escala LRINEC es un instrumento reproducible para el diagnóstico de infecciones necrosantes de partes blandas y está relacionada con el número de complicaciones y la morbilidad ortopédica, aunque no necesariamente con la cantidad de cirugías realizadas.
Palabras clave: Infección necrosante; escala LRINEC; morbilidad; fascitis necrosante.
Nivel de Evidencia: II
Descargas
Métricas
Detalles del artículo
La aceptación del manuscrito por parte de la revista implica la no presentación simultánea a otras revistas u órganos editoriales. La RAAOT se encuentra bajo la licencia Creative Commons 4.0. Atribución-NoComercial-CompartirIgual (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/deed.es). Se puede compartir, copiar, distribuir, alterar, transformar, generar una obra derivada, ejecutar y comunicar públicamente la obra, siempre que: a) se cite la autoría y la fuente original de su publicación (revista, editorial y URL de la obra); b) no se usen para fines comerciales; c) se mantengan los mismos términos de la licencia.
En caso de que el manuscrito sea aprobado para su próxima publicación, los autores conservan los derechos de autor y cederán a la revista los derechos de la publicación, edición, reproducción, distribución, exhibición y comunicación a nivel nacional e internacional en las diferentes bases de datos, repositorios y portales.
Se deja constancia que el referido artículo es inédito y que no está en espera de impresión en alguna otra publicación nacional o extranjera.
Por la presente, acepta/n las modificaciones que sean necesarias, sugeridas en la revisión por los pares (referato), para adaptar el trabajo al estilo y modalidad de publicación de la Revista.
Citas
2. Lancerotto L, Tocco I, Salmaso R, Vindigni V, Bassetto F. Necrotizing fasciitis: classification, diagnosis, and
management. J Trauma 2012;72(3):560-6. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0b013e318232a6b3
3. Tunovic E, Gawazuik J, Bzura T, Embil J, Esmail A, Logsetty S. Necrotizing fasciitis: A six-year experience. J Burn
Care Res 2012;33(1):93-100. https://doi.org/10.1097/BCR.0b013e318239d571
4. Lee A, May A, Obremskey WT. Necrotizing soft-tissue infections: an orthopaedic emergency. J Am Acad Orthop
Surg 2019;27(5): e199-e206. https://doi.org/10.5435/JAAOS-D-17-00616
5. Magala J, Makobore P, Makumbi T, Kaggwa S, Kalanzi E, Galukande M. The clinical presentation and early
outcomes of necrotizing fasciitis in a Ugandan Tertiary Hospital–a prospective study. BMC Res Notes 2014;7:476.
https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-0500-7-476
6. Misiakos EP, Bagias G, Patapis P, Sotiropoulos D, Kanavidis P, Machairas A. Current concepts in the management of necrotizing fasciitis. Front Surg 2014;1:36. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsurg.2014.00036
7. Shiroff AM, Herlitz GN, Gracias VH. Necrotizing soft tissue infections. J Intensive Care Med 2014;29(3):138-44.
https://doi.org/10.1177/0885066612463680
8. Wong C-H, Khin L-W, Heng K-S, Tan K-C, Low C-O. The LRINEC (laboratory risk indicator for necrotizing
fasciitis) score: a tool for distinguishing necrotising fasciitis from other soft-tissue infections. Crit Care Med 2004;
32(7):1535-41. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ccm.0000129486.35458.7d
9. Wilson MP, Schneir AB. A case of necrotizing fasciitis with a LRINEC score of zero: clinical suspicion should
trump scoring systems. J Emerg Med 2013;44(5):928-31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jemermed.2012.09.039
10. Holland MJ. Application of the laboratory risk indicator in necrotising fasciitis (LRINEC) score to patients in a
tropical tertiary referral centre. Anaesth Intensive Care 2009; 37(4): 588-92. https://doi.org/10.1177/0310057X0903700416
11. Hakkarainen TW, Kopari NM, Pham TN, Evans HL. Necrotizing soft tissue infections: review and current concepts in treatment, systems of care, and outcomes. Curr Probl Surg 2014; 51: 344-62. https://doi.org/10.1067/j.cpsurg.2014.06.001
12. Tsai Y-H, Hsu RW-W, Huang K-C, Huang T-J. Laboratory indicators for early detection and surgical treatment of vibrio necrotizing fasciitis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2010;468(8):2230-7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-010-1311-y
12. Chao W-N, Tsai S-J, Tsai C-F, Su C-H, Chan K-S, Lee Y-T, et al. The Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotizing
Fasciitis score for discernment of necrotizing fasciitis originated from Vibrio vulnificus infections. J Trauma Acute
Care Surg 2012;73(6): 1576-82. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0b013e318270d761
14. Liao C-I, Lee Y-K, Su Y-C, Chuang C-H, Wong C-H. Validation of the laboratory risk indicator for necrotizing
fasciitis (LRINEC) scorefor early diagnosis of necrotizing fasciitis. Tzu Chi Medical J 2012;24(2):73-6. https://doi.
org/10.1016/j.tcmj.2012.02.009
15. Borschitz T, Schlicht S, Siegel E, Hanke E, von Stebut E. Improvement of a clinical score for necrotizing fasciitis:
‘Pain out of proportion’ and high CRP levels aid the diagnosis. PLoS One 2015;10(7):e0132775. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0132775
16. Bechar J, Sepehripour S, Hardwicke J, Filobbos G. Laboratory risk indicator for necrotising fasciitis (LRINEC)
score for the assessment of early necrotising fasciitis: a systematic review of the literature. Ann R Coll Surg Engl
2017;99(5):341-6. https://doi.org/10.1308/rcsann.2017.0053