Catastrophic Spinal Cord Injuries in Argentine Rugby. Impact of the Measures Implemented and Their Relative Reduction in Time
Main Article Content
Abstract
Materials and Methods: Data obtained from a telephone survey carried out in the collaborative framework between the Union Argentina de Rugby and the Fundación para la Lucha de Enfermedades Neurológicas de la Infancia (Fleni, by its acronym) were analyzed. We carried out a qualitative analysis of the data and their relationship to progressive changes in sports regulations.
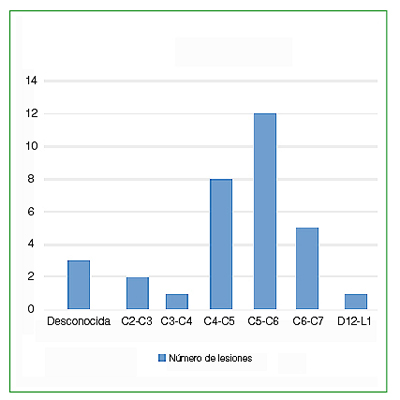
Results: It was observed that the number of injuries remained stable year after year. When associating this fact with a sustained increase in the number of players per year, we can see a relative decrease in the risk of injury.
Conclusion: Catastrophic injuries have a great impact on the quality of life of the player and his environment. They must be considered inadmissible and the efforts must be increased to achieve zero risk. In recent years, multiple preventive measures have been implemented and regulations have been modified in order to avoid catastrophic injuries.
Downloads
Metrics
Article Details
Manuscript acceptance by the Journal implies the simultaneous non-submission to any other journal or publishing house. The RAAOT is under the Licencia Creative Commnos Atribución-NoComercial-Compartir Obras Derivadas Igual 4.0 Internacional (CC-BY-NC.SA 4.0) (http://creativecommons.org/licences/by-nc-sa/4.0/deed.es). Articles can be shared, copied, distributed, modified, altered, transformed into a derivative work, executed and publicly communicated, provided a) the authors and the original publication (Journal, Publisher and URL) are mentioned, b) they are not used for commercial purposes, c) the same terms of the license are maintained.
In the event that the manuscript is approved for its next publication, the authors retain the copyright and will assign to the journal the rights of publication, edition, reproduction, distribution, exhibition and communication at a national and international level in the different databases. data, repositories and portals.
It is hereby stated that the mentioned manuscript has not been published and that it is not being printed in any other national or foreign journal.
The authors hereby accept the necessary modifications, suggested by the reviewers, in order to adapt the manuscript to the style and publication rules of this Journal.
References
https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-444-63954-7.00004-5
2. Fuller CW. Catastrophic injury in rugby union: is the level of risk acceptable? Sports Med 2008;38(12):975-86.
https://doi.org/10.2165/00007256-200838120-00002
3. Chan CW, Eng JJ, Tator CH, Krassioukov A. Epidemiology of sport-related spinal cord injuries: A systematic
review. J Spinal Cord Med 2016;39(3):255-64. https://doi.org/10.1080/10790268.2016.1138601
4. Secin FP, Poggi EJ, Luzuriaga F, Laffaye HA. Disabling injuries of the cervical spine in Argentine rugby over the
last 20 years. Brit J Sports Med 1999;33(1):33-6. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsm.33.1.33
5. Reboursiere E, Bohu Y, Retière D, Sesboüé B, Pineau V, Colonna JP, et al. Impact of the national prevention policy and scrum law changes on the incidence of rugby-related catastrophic cervical spine injuries in French Rugby Union. Brit J Sports Med 2016;52(10):674-7. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2016-096122
6. Badenhorst M, Verhagen E, Lambert M, Mechelen WV, Brown J. When this happens, you want the best care:
Players’ experiences of barriers and facilitators of the immediate management of rugby-related acute spinal cord injury. Qual Health Res 2019;29(13):1862-76. https://doi.org/10.1177/1049732319834930
7. Quarrie KL, Cantu RC, Chalmers DJ. Rugby union injuries to the cervical spine and spinal cord. Sports Med
2002;32(10):633-53. https://doi.org/10.2165/00007256-200232100-00003
8. Trewartha G, Preatoni E, England ME, Stokes KA. Injury and biomechanical perspectives on the rugby scrum: a
review of the literature. Brit J Sports Med 2014;49(7):425-33. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2013-092972
9. Fiorillo P, Demonti H, Giuria H, Aparicio JL, Della Vedova F. Trauma deportivo cervical catastrófico en un jugador de rugby. Rev Asoc Argent Traumatol Dep 2014:21 (1). Disponible en: https://g-se.com/trauma-deportivo-cervicalcatastrofico-en-un-jugador-de-rugby-1821-sa-H57cfb27254339
10. Badenhorst M, Verhagen EA, Mechelen WV, Lambert MI, Viljoen W, Readhead C, et al. A comparison of
catastrophic injury incidence rates by Provincial Rugby Union in South Africa. J Sci Med Sport 2017;20(7):643-7.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsams.2017.01.232
11. Badenhorst M, Brown JC, Lambert MI, Mechelen WV, Verhagen E. Quality of life among individuals with rugbyrelated spinal cord injuries in South Africa: a descriptive cross-sectional study. BMJ Open 2018;8(6):e020890. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2017-020890
12. Quarrie KL, Gianotti SM, Hopkins WG, Hume PA. Effect of nationwide injury prevention programme on serious
spinal injuries in New Zealand rugby union: ecological study. BMJ 2007;334(7604):1150. https://doi.org/10.1136/
bmj.39185.605914.ae