Medium-term results of the rotary hinged prosthesis in total primary and revision knee replacement.
Main Article Content
Abstract
The aim of the study was analyse the clinical and radiological mid-term outcomes of 34 rotating hinge knee arthroplasty.
Materials and Method
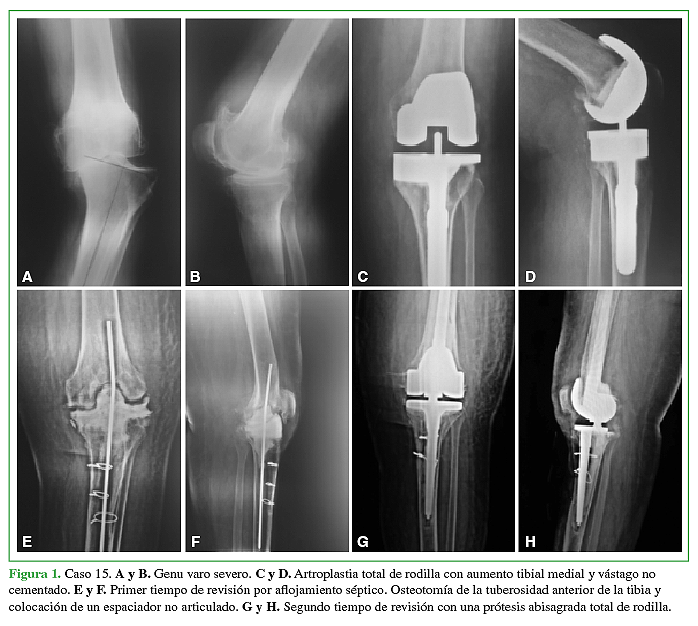
We study 34 hinge knee prostheses. The indication for surgery was in the setting of primary surgery for 10 patients (29.5%) and in setting of revision for 24 patients (70.5%). The mean age was 78.5 years (range 54–85 years).
Results
The mean follow-up was 6.5 years (range 2 -12 years). The range of motion achived was 110º of flexion (range 70º – 130º) and 5º of extensión (range 0º-20º). The Knee Society (KSS) Score improved from 38 in the preoperative to 82 in the postoperative. Radiolucent lines around the femoral or tibial components were observed in 8 patients (23%). Five out of 34 (14.7%) patients developed complications. Three (8.9%) developed a deep infection. Two (5.9%) developed patellofemoral complications. Prosthetic survivorship for revisión was 94% at 6.5 years. Prosthetic survivorship for aseptic loosening was 100%.
Conclusion
Moderns rotating knee hinge provides good results in terms of function and pain relief with a low rate of aseptic loosening. However deep infection and septic loosening are frequent.
Downloads
Metrics
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Manuscript acceptance by the Journal implies the simultaneous non-submission to any other journal or publishing house. The RAAOT is under the Licencia Creative Commnos Atribución-NoComercial-Compartir Obras Derivadas Igual 4.0 Internacional (CC-BY-NC.SA 4.0) (http://creativecommons.org/licences/by-nc-sa/4.0/deed.es). Articles can be shared, copied, distributed, modified, altered, transformed into a derivative work, executed and publicly communicated, provided a) the authors and the original publication (Journal, Publisher and URL) are mentioned, b) they are not used for commercial purposes, c) the same terms of the license are maintained.
In the event that the manuscript is approved for its next publication, the authors retain the copyright and will assign to the journal the rights of publication, edition, reproduction, distribution, exhibition and communication at a national and international level in the different databases. data, repositories and portals.
It is hereby stated that the mentioned manuscript has not been published and that it is not being printed in any other national or foreign journal.
The authors hereby accept the necessary modifications, suggested by the reviewers, in order to adapt the manuscript to the style and publication rules of this Journal.
References
2. Duquennoy A, Decoulx J, Epinette JA, Letendart J. Hinge pros- thesis of the knee. Apropos of 185 cases. Rev Chir Orthopt 1983;69(6):465—74.
3. Pradhan NR, Bale L, Kay P, Porter ML Salvage revision total knee replacement using the Endo-Model rotating hinge prosthesis. Knee. 2004;11:469–473.
4. Fahad Hossain MRCS, Shelain Patel MRCS, Fares Sami Haddad FRCS Midterm Assessment of Causes and Results of Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res (2010) 468:1221–1228
5. Barrack RL. Evolution of the rotating hinge for complex total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001; 392:292-299.
6. Joshi N, Navarro-Quilis A. Is there a place for rotating-hinge arthroplasty in knee revi- sion surgery for aseptic loosening [published online ahead of print April 14, 2011]? J Arthroplasty. 2008; 23(8):1204-1211.
7. E. Carlos Rodrıguez-Merchan MD, PhD, Primitivo Gomez-Cardero MD, Angel Martınez-Lloreda MD Revision knee arthroplasty with a rotating-hinge design in elderly patients with instability following total knee arthroplasty. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2015 Mar;6(1):19-23
8. Daniel Hernandez-Vaquero PhD, Manuel A. Sandoval-Garcıa PhD. Hinged Total Knee Arthroplasty in the Presence of Ligamentous Deficiency. Clin Orthop Relat Res (2010) 468:1248–1253
9. Westrich GH, Mollano AV, Sculco TP, Buly RL, Laskin RS, Windsor R. Rotating hinge total knee arthroplasty in severely affected knees. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000; (379):195-208.
10. Pour AE, Parvizi J, Slenker N, Purtill JJ, Sharkey PF. Rotating hinged total knee replacement: use with caution. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007; 89(8):1735-1741.
11. B. Guenoun, L. Latargez, M. Frelson, G. Defossez. Complication following rotating hinge Endo-Model (Link) knee arthroplasty. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2009 Nov;95(7):529-36.
12. Insall JN, Dorr LD, Scott RD, Scott WN. Rationale of the Knee Society clinical rating system. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989;248:13-4.
13. Fernando Bidolegui, Guillermo Arce, Alfonso Lugones, Sebastián Pereira and Gabriel Vindver. Tranexamic Acid Reduces Blood Loss and Transfusion in Patients Undergoing Total Knee Arthroplasty without Tourniquet: A Prospective Randomized Controlled Trial. The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2014, 8, 250-254
14. Keblish PA. Valgus deformity in TKR: The lateral retinacular approach. Orthop. Trans. 1985, 9:28.
15. T. Gehrke, D. Kendoff, C. Haasper. Management factorials in total knee arthroplasty The role of hinges in primary total knee replacement. Bone Joint J 2014;96-B(11 Suppl A):93–5.
16. Cottino U, Abdel MP, Perry KI, Mara KC, Lewallen DG, Hanssen AD. Long-Term Results After Total Knee Arthroplasty with Contemporary Rotating-Hinge Prostheses. Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017 Feb 15;99(4):324-330
17. Springer BD1, Hanssen AD, Sim FH, Lewallen DG. The kinematic rotating hinge prosthesis for complex knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001 Nov;(392):283-91.
18. Springer BD1, Sim FH, Hanssen AD, Lewallen DG.The modular segmental kinematic rotating hinge for nonneoplastic limb salvage. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004 Apr;(421):181-7.