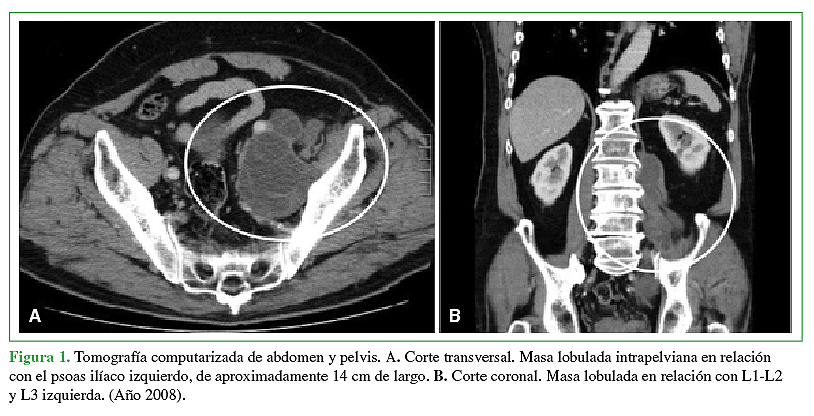
Intradural vertebral hydatidosis. A medical-surgical pathology. Report of two cases.
Main Article Content
Abstract
The treatment is usually medical-surgical with disparate clinical results due to high rate of recurrences and sequelae.
Experience in the management of patients affected with intradural hydatidosis is limited because of their low frequency. Therefore we wanted to report 2 cases observed in our center and to analyze the progress in its management.
Downloads
Metrics
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Manuscript acceptance by the Journal implies the simultaneous non-submission to any other journal or publishing house. The RAAOT is under the Licencia Creative Commnos Atribución-NoComercial-Compartir Obras Derivadas Igual 4.0 Internacional (CC-BY-NC.SA 4.0) (http://creativecommons.org/licences/by-nc-sa/4.0/deed.es). Articles can be shared, copied, distributed, modified, altered, transformed into a derivative work, executed and publicly communicated, provided a) the authors and the original publication (Journal, Publisher and URL) are mentioned, b) they are not used for commercial purposes, c) the same terms of the license are maintained.
In the event that the manuscript is approved for its next publication, the authors retain the copyright and will assign to the journal the rights of publication, edition, reproduction, distribution, exhibition and communication at a national and international level in the different databases. data, repositories and portals.
It is hereby stated that the mentioned manuscript has not been published and that it is not being printed in any other national or foreign journal.
The authors hereby accept the necessary modifications, suggested by the reviewers, in order to adapt the manuscript to the style and publication rules of this Journal.
References
2. Zlitni M, Ezzaouia K, Lebib H, Karray M, Kooli M et al. Hydatid cyst of bone: diagnosis and treatment. World J Surg. 2001;25:75-82.
3. Schneppenheim M, Jerosch J. Echinococcosis granulosus/cysticus of the tibia. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2003;123:107-11.
4. Martínez A, Herrera A, Cuenca J, Herrero L. Hydatidosis of the pelvis and hip. Int Orthop. 2001;25:302-4.
5. Y. Yildiz, K. Bayrakci, M. Altay, Y. Saglik. The use of polymethylmethacrylate in the management of hydatid disease of bone J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 2001;83:1005-8.
6. Wen H, Zhang HW, Muhumut M, Zou PF, Craig PS. Initial observation on albendazole in combination with cimetidine for the treatment of human cystic echinococcosis. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1994; 88:49–52.
7. Jamshidi M, Mohraz M, Zangeneh M, Jamshidi A. The effect of combination therapy with albendazole and praziquantel on hydatid cyst treatment. Parasitology Research. 2008;103:195-199.
8. Islekel S, Zileli M, Ersahin Y. Intradural spinal hydatid cysts. Eur. Spine J. 1998;7:162-164.
9. Altinors N, Bavbek M, Caner H. Central nervous system hydatidosis in Turkey: a cooperative study and literature survey analysis of 458 cases. J Neurosurg. 2000; 93: 1-8.
10. Braithwaite P, Less R. Vertebral Hydatid disease. Radiological assessment. Radiology 1981; 140: 763-766.
11. Kaen A, Lagares A, Perez Nuñez A. Intradural Extramedullary spinal hidatidosis: case report. Neurocirugia 2009; 20: 282-287.
12. Song X, Ding L, Wen H. Bone Hydatidic Disease. Postgrad Med J. 2007 Aug;83(982):536-42.
13. Ozdemir H, Ogun T, Tasbas B. A lasting solution is hard to achieve in primary hydatid disease of the spine. Spine. 2004;29:932–937.
14. Fica A, Soto A, Slater J, Peralta M, Humeres R et al. Quince años de experiencia clínica con hidatidosis. Rev chilena Infectol, 2012; 29:183-191.